The ribbon is present in Microsoft Word 2007, Excel 2007, PowerPoint 2007, Access 2007 and some Outlook 2007 windows. The ribbon is not user customizable in Office 2007. Each application has a different set of tabs that exposes functions that the application offers. Office 2007 include applications such as Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Outlook. They're available as a one-time purchase for use on a single PC. Microsoft 365 plans include premium versions of these applications plus other services that are enabled over the internet, including online storage with OneDrive and Skype minutes for home use.
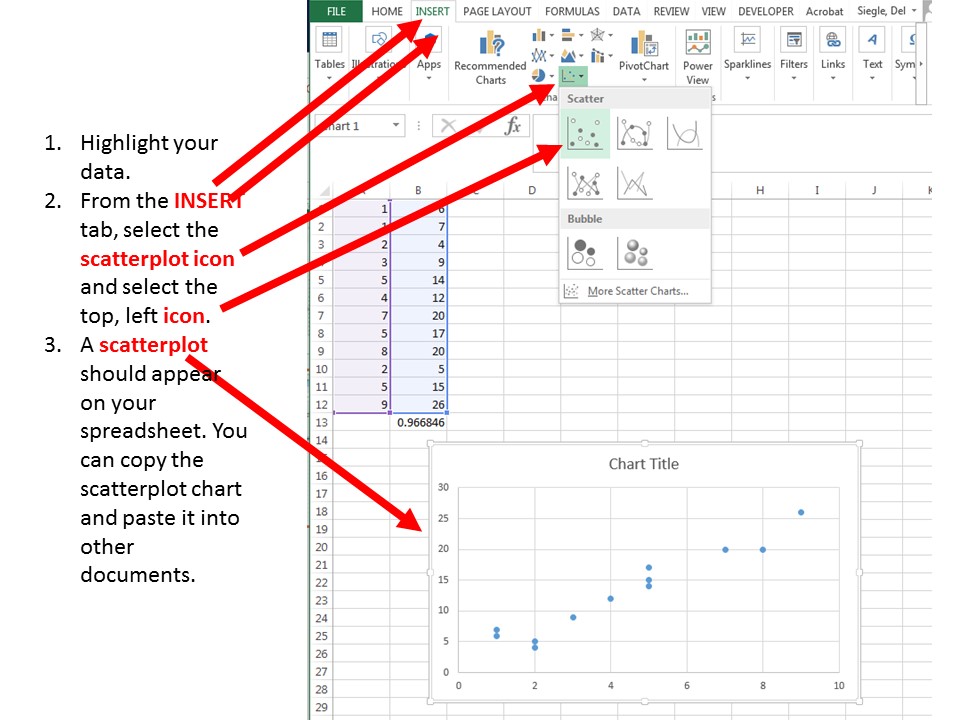
This article is based on legacy software.
The Subtotal function allows you to set up a calculation in your worksheet. Then, by filtering the data, the same calculation is performed on subsets of your data. The Subtotal function ignores values in rows hidden by a filter. It can be used with Tables or any range of data.
Using the Subtotal Function
The Subtotal function is easily created with the Function Arguments dialog box. The first piece of information you will need is the Function Numbers. This determines what type of calculation will be performed.
Open the desired worksheet.
Drive for time machine backup. Select the cell where you want the result of the function to appear.
NOTE: If you are filtering your worksheet, make sure that the selected cell is below your data. This allows you to see the results.Click Toolbox.
The Formula Builder appears.In the Search for a function text box, type Subtotal.
OR
Scroll to the Math and Trigonometry section.Double click Subtotal.
The Arguments section appears on the Formula Builder.In the function_num text box, type the number of the function you would like to perform.
HINT: For more information, refer to Function Numbers.In the ref1text box, type the range of cells to be analyzed.
OR
Select the range of cells to include.Press [return].
The subtotal appears in the selected cell and the formula appears in the FormulaBar.
EXAMPLE: In the formula =SUBTOTAL(1,D2:D11), 1 designates the calculation from the function_numtext box as an average, and D2:D11 designates the cell range from the ref1 text box.
Microsoft Office Word Excel 2007
Using a Filter to Analyze Subsets
If you have applied a Subtotal function to a section of your worksheet and want to see results for a specific category of information contained within that subtotal, you can hide rows by filtering the field. After filtering, the function will calculate with only the rows that are visible, allowing you to see customized results. For more information on filtering, refer to Filtering Your Database.
Click within the row of column headings.
From the Data menu, select Filter » Autofilter.
Pull-down menus appear in each of the selected cells.On the desired column, from the pull-down list, select the desired option.
EXAMPLE: If you only wanted to work with entries that were registered on June 1st, 2008, selecting 6/1/08 would hide all entries that were not registered on that date.
Modifying the Subtotal Function
Once you perform one of the Subtotal calculations on your data, you can change the calculation at any time by modifying the existing function. This allows you to perform additional calculations on the same data.
Select the cell where the Subtotal function is being performed.
The function appears in the FormulaBar.On the Formula Builder, in the Arguments section, in the function_num text box, change the value.
HINT: Choose from the list of possible calculations below.Press [return].
Function Numbers
The Subtotal function allows you to work several different calculations on your selected data. Windows media player 9 0 o posterior. In order for the function to work correctly, you will need to use the number of the correct calculation when prompted.
| # | Calculation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AVERAGE | Adds all entries and then divides by the number of entries. |
| 2 | COUNT | Counts the number of entries containing numbers. |
| 3 | COUNTA | Counts the number of entries that are not blank (includes text entries). |
| 4 | MAX | Reports the highest number of all the entries. |
| 5 | MIN | Reports the lowest number of all the entries. |
| 6 | PRODUCT | Multiplies all the entries together. |
| 7 | STDEV | Computes the standard deviation, assuming the selection is a sample of the entire population. |
| 8 | STDEVP | Computes the standard deviation, assuming the selection is the entire population. |
| 9 | SUM | Adds all entries together. |
| 10 | VAR | Computes the variance, assuming the selection is a sample of the entire population. |
| 11 | VARP | Computes the variance, assuming the selection is the entire population. |
Microsoft Excel 2007 Online
An Example
The example below shows data about employees' time worked in particular pay periods. With this unfiltered data, the Subtotal function used at the bottom of the Hours column reflects the maximum number of hours worked by any employee.
The image below shows the results of filtering the data. After applying a filter so that only Justin's information is visible, the Subtotal function calculates the maximum hours that Justin worked.
